You can contact us via our social media accounts, phone numbers and our application form on our website and make an appointment.
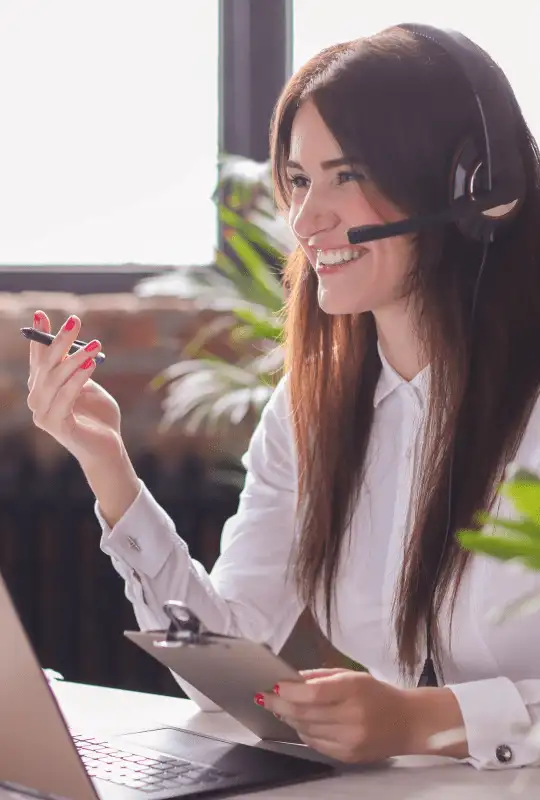

After you contact us, we organize your entire treatment process specially for you and plan your transfer, accommodation and treatment together.

24/7 assistance throughout the stay is a very important issue for the patient and their family. With our Professional Guidance Service, we offer support throughout this treatment process, such as guiding the patient, organizing medical appointments, facilitating communication and providing translation services if needed.

We will meet with you online or in person to learn more about your health condition and possible treatment options, answer your questions and work with you to create the most effective and customized treatment plan.

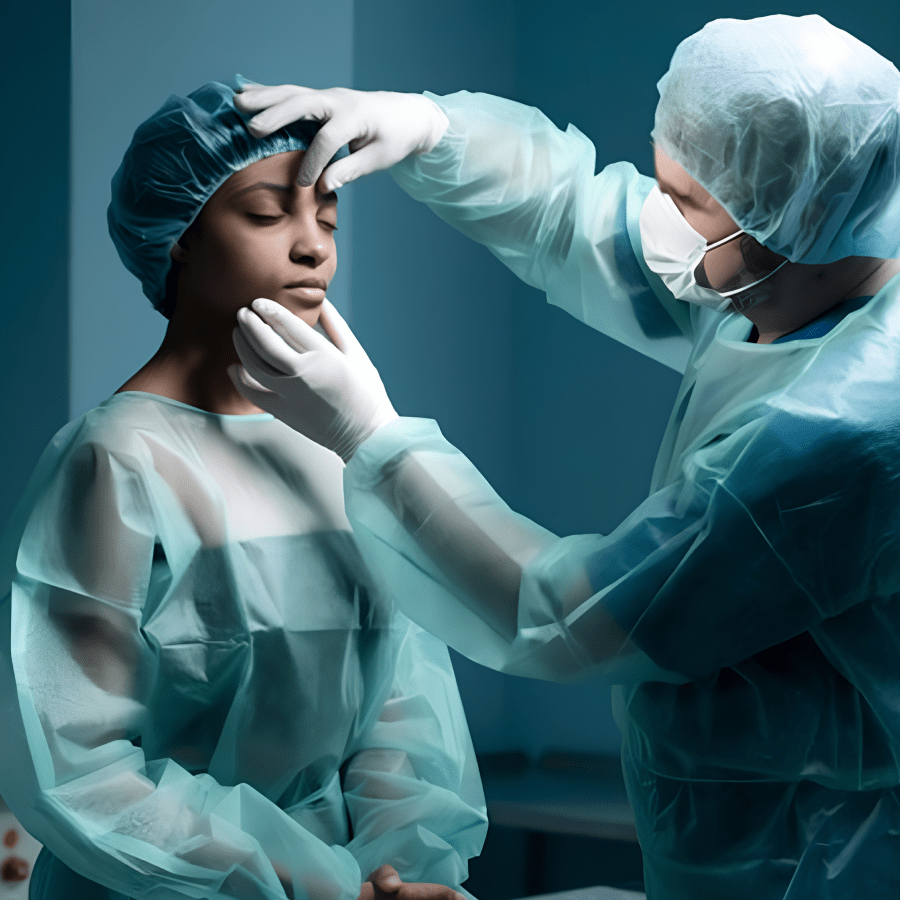
With our state-of-the-art devices, we perform your operation in a professional manner, prioritizing patient safety and satisfaction.